Aquaponics is an environmentally friendly method of growing plants and can be done in a much smaller space than conventional farming techniques.
The name is derived from the fact that this system merges aquaculture and hydroponics, the results can be impressive.
Aquaculture
This is the farming of fish in controlled conditions. Common examples are prawns and crayfish although any aquatic creature can be farmed.
Hydroponics
Hydroponics focuses on growing plants without soil. This is usually achieved by allowing the roots of the plants to sit in a solution of water and minerals.
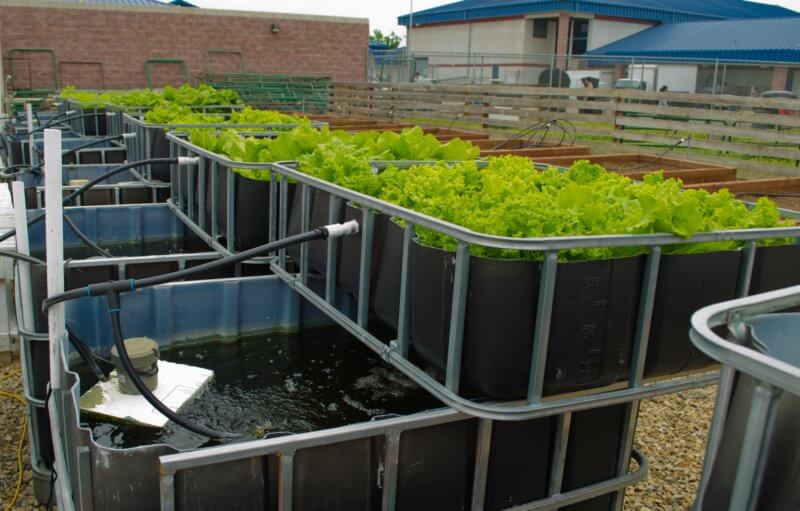
Basic Aquaponics System
Aquaponics takes both these systems and harmonizes them, allowing you to grow plants in a small space and, if you wish, breed fish at the same time.
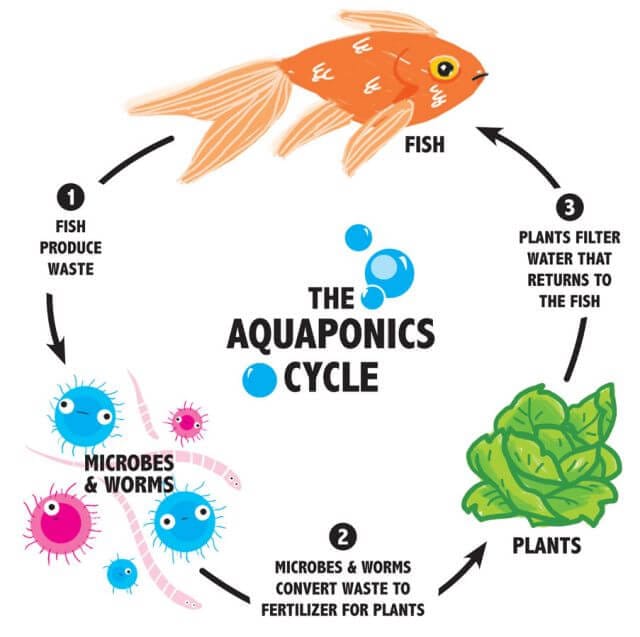
A basic system would comprise of one tank with fish in. The fish are fed in the same way as you would look after pet fish. These fish produce waste which is contained in the water.
The water is then pumped from one tank to another, carrying the fish waste with it.
Your second tank will contain a growing media, this is not soil. The grow media captures fish waste. The same growing media also contains bacteria, which is essential to the success of your system.
These bacteria convert the ammonia and nitrites from the fish waste into nitrates, which plants can use as food. It’s an essential part of the process as the plants can’t survive or flourish without these nitrates.
The plants absorb the nitrates, effectively cleaning the water for the fish. This clean water is cycled back to the fish tank, keeping the fish healthy.
The beauty of an aquaponics system is that you only need to feed the fish, everything else takes care of itself.
A simple aquaponics system requires some supplies. These are the fish tank, a pump, a second tank with growing media, plants, and pipes to connect the two tanks.
Flood & Drain Versus Continuous
Water needs to leave your fish tank and get to the plants. There are two ways of doing this. The first is the continuous approach. This is when the water circulates around the system continually. It soaks the lower part of the growing media to leave the fish waste. Because part of the growing media is exposed to the air it has the oxygen and bacteria needed to convert the waste into plant nutrition.
The alternative to continually pumping water round is to flood the grow media for approximately 15 minutes every hour. This is known as the flood and drain approach. Water is pumped from the tank to cover the grow media and then naturally drains back to the fish tank before the cycle is repeated.
Both methods are effective.
Types Of Aquaponic System
However, once you decide to try aquaponics you’ll need to understand there are several different ways of creating a system, all can be successful. The choice of system is personal and can be adapted to suit your own needs.
- Media Filled Beds
This is the simplest approach and what has been described above. The plant grow beds are filled with growing media and the plants placed into it. Nutrient-rich water reaches the plant roots via continuous water flow or the flood and drain approach.
It’s a great system to start out with.
- Deep Water Culture
Large water beds are created and the plants simply float on the surface, their roots dangle in the water. This gives them all the nutrients they need. The water is pumped around continually and has to go through a filtration system between the fish tank and the growing area. This removes large waste and facilitates the conversion of fish waste to plant nutrients. The system needs a lot of airstones under the floating rafts in order for the roots not to rot.
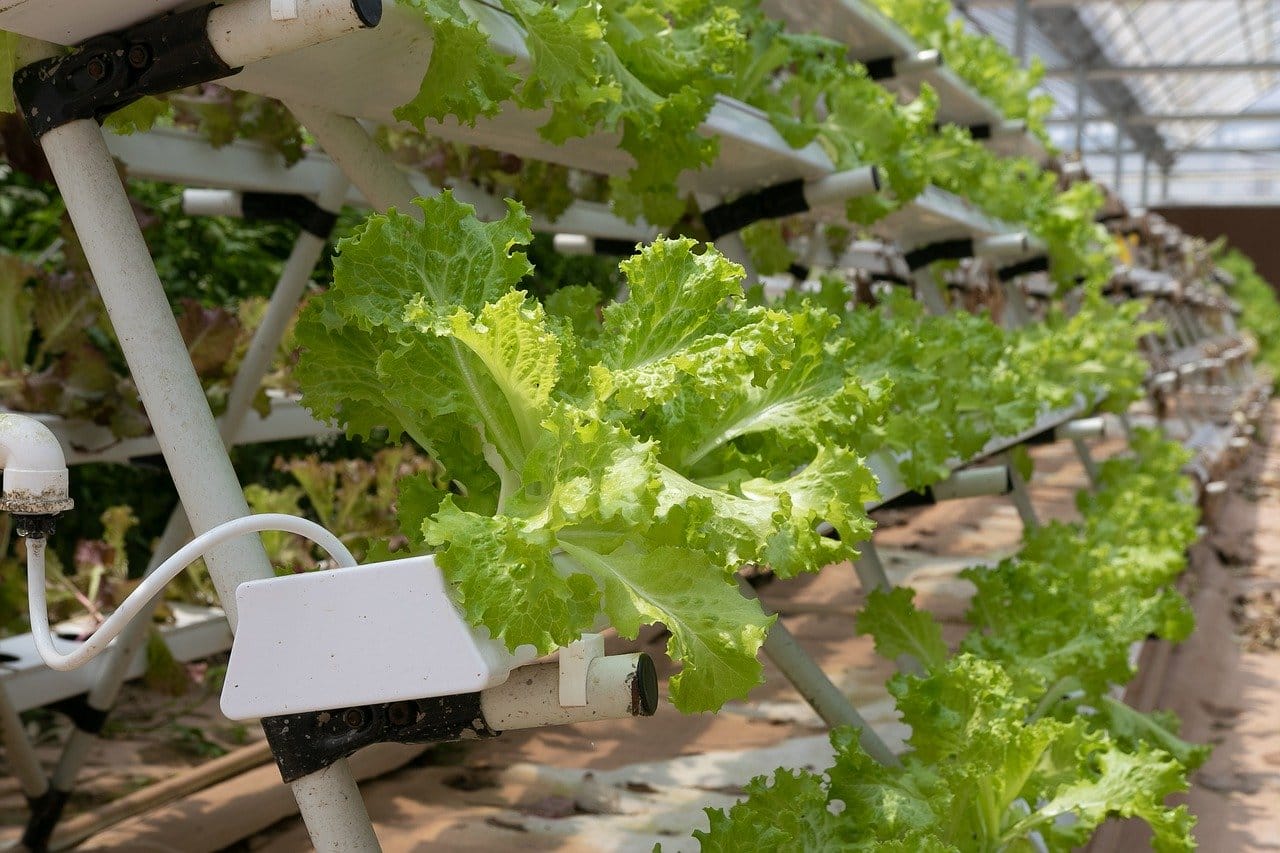
- Nutrient Flow Technique -NFT
This is a similar approach to deep water culture but instead of the plants floating on the water they are positioned in gutters and a constant trickle of water comes through the gutter. Plants will have their roots in the trickle.
However, because they are planted into small waterways this approach is best suited for plants with small root clusters, such as lettuce.
Essential Maintenance
Feeding the fish is the only real cost but it’s not the only thing you need to do if you want your aquaponics system to be successful.
- Water quality
Your fish need to have clean water to keep them healthy. This is what the bacteria are supposed to do but you’ll need to regularly check the water quality to ensure the environment is right for your chosen fish.
Potentially more important is the pH level. The exact pH level that suits your system will depend on the fish you’re keeping and the plants you’re trying to grow. But, if your system is too acidic or alkaline your fish, bacteria and plants will die. It’s important to note that any change to pH must be done gradually or you’ll kill the fish and then your plants. In general, the pH will need to be between 6.8 and 7.4.
This is actually the reason most people start with tilapia or goldfish, they are generally very tolerant even if the water quality is not quite right.
- Ammonia
Ammonia enters the system from fish urine and decomposing feces. The bacteria in your system converts the ammonia into food for the plants. But, if it doesn’t do this effectively the ammonia levels could rise, which is fatal for your fish.
Equally, low levels of ammonia can mean there are not enough nutrients for the bacteria to feed on, slowing the growth of the plants.
- Oxygen Levels
The level of dissolved oxygen should be around 5 ppm or higher, this is sufficient to keep your fish healthy. If it drops below this you can add an air pump or stone to sort the issue.
- Water Temperature
This will depend on the fish you keep. Tilapia generally prefer 65°F to 85°F, which means you need a water heater. Trout are also hardy but prefer cooler temperatures, between 55°F and 65°F.
Final Thoughts
Initially, it can seem daunting to establish an aquaponics system. But, the basics remain simple, a fish tank, pumps, and pipes to a second tank, grow media, and your plants.
Regular checks on water quality are essential but, you’ll find in most cases you don’t need to do anything other than a check. This allows you to spot changes and make small adjustments to feeding, water flow, or even the number of fish.
In short, aquaponics is productive and fun, with plenty of opportunities to adapt the system to your own needs and style.
Bio:
Nick Brooke is the author of Aquaponics for Beginners. What started as a hobby has grown to a popular aquaponics website, with thousands of monthly readers coming to his website to discover aquaponics.